Traditional COB Technology
Traditional Chip on Board (COB) technology is a method of mounting and connecting LED chips directly to a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) without the use of a traditional package. Here’s a detailed explanation of traditional COB technology.
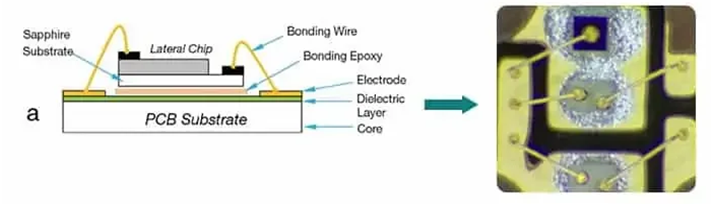
- Basic Concept
In traditional COB technology, individual LED chips are directly attached to the PCB substrate. The LED die, which is the actual semiconductor device that emits light, is bonded to the PCB using a conductive adhesive or solder. The connections between the LED die and the PCB are made using wire bonding.
- Assembly Process
- Chip Placement: LED chips are precisely placed on the PCB in a predetermined pattern. This is often done using automated placement machines.
- Wire Bonding: Thin gold or aluminum wires are used to connect the LED chip’s electrodes to the PCB. These wires are bonded to the chip and the PCB pads using ultrasonic bonding techniques.
- Encapsulation: The LED chips and wire bonds are usually encapsulated with a protective resin or silicone to safeguard against environmental factors and mechanical damage. This also helps to distribute light more evenly and improve optical performance.
- Testing and Packaging: After assembly, the LED modules are tested for electrical and optical performance. They may be integrated into larger lighting systems or sold as standalone components.
- Key Characteristics
- Cost Effectiveness: Traditional COB is relatively cost-effective compared to advanced technologies like Flip Chip COB. It uses established manufacturing processes and materials.
- Thermal Management: Thermal management relies on the thermal conductivity of the PCB and any additional heat sinks or thermal management materials used. The wire bonds can introduce thermal resistance, which may affect performance and longevity.
- Size and Density:The technology allows for high-density LED arrangements on a single PCB, which can lead to high light output and compact designs.
- Performance:While traditional COB technology offers good performance, it may be limited by the thermal and electrical characteristics of the wire bonds and the PCB.
- Reliability:The reliability of traditional COB can be affected by the mechanical stress on the wire bonds and thermal cycling, which can lead to potential failures over time.
- Applications
- General Lighting:Traditional COB LEDs are widely used in general lighting applications, such as street lights, office lighting, and residential fixtures.
- LED Modules:They are also used in LED modules for various applications, including spotlights, downlights, and floodlights.
- Cost-Sensitive Applications:Due to its lower cost, traditional COB is often chosen for applications where cost is a critical factor, and slightly lower performance is acceptable.
- Advantages and Disadvantage
- Advantage:
- Established Technology: Well-understood and widely used in the industry.
- CostEffective: Lower production costs compared to more advanced technologies.
- High Light Output: Capable of delivering high levels of light output due to high-density chip placement.
- Disadvantage:
- Thermal Management Issues: Less efficient thermal management due to wire bonds and PCB limitations.
- Mechanical Reliability: Wire bonds can be susceptible to mechanical stress and thermal fatigue.
- Lower Efficiency: May have lower electrical efficiency and light output compared to more advanced technologies like Flip Chip COB.
Traditional COB technology remains popular due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce high-intensity lighting. However, for applications requiring higher performance and reliability, alternative technologies such as Flip Chip COB might be considered.
Flip chip COB Technology
Flip Chip ChiponBoard (Flip Chip COB) technology is an advanced method of mounting and connecting LED chips to a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) that offers several advantages over traditional COB technology. Here’s an in-depth explanation of Flip Chip COB technology:
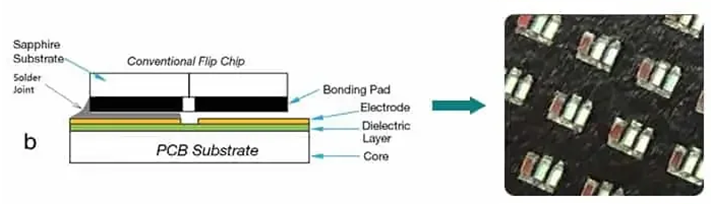
- Basic Concept
In Flip Chip COB technology, LED chips are flipped upside down and directly mounted onto the PCB. Instead of using wire bonds for electrical connections, solder bumps on the underside of the LED chips make direct contact with corresponding pads on the PCB.
- Assembly Process
- Chip Placement:The LED chips are flipped so that the active side (the side with the semiconductor junction) faces down toward the PCB. These chips are precisely aligned and placed onto the PCB.
- Solder Bumping: The LED chips are prefabricated with solder bumps on their underside. These bumps act as both electrical and thermal connections.
- Re-flow Soldering:The PCB with the placed chips is then heated in a reflow oven. The heat melts the solder bumps, which solidify upon cooling to form reliable electrical connections between the chip and the PCB.
- Encapsulation:After soldering, the chips and solder joints are encapsulated with a protective resin or silicone to enhance durability and optical performance. This encapsulation also protects the chip from environmental factors.
- Testing and Integration:The assembled LED modules are tested for performance, including electrical characteristics and light output. They are then integrated into final lighting products or systems.
- Key Characteristics
- Thermal Management:Flip Chip COB technology offers superior thermal management compared to traditional COB. The direct contact between the chip’s backside and the PCB allows for better heat dissipation, reducing the thermal resistance and improving overall performance.
- Electrical Performance:The direct solder bumps provide lower electrical resistance and inductance, leading to improved electrical performance and efficiency.
- Size and Density:Flip Chip COB allows for very compact designs and high-density chip arrangements, as no wire bonds are taking up space.
- Reliability:With no wire bonds, Flip Chip COB technology reduces the potential points of failure. This enhances the mechanical reliability and durability of the LED module.
- Applications
- High-Performance Lighting:Due to its superior thermal management and efficiency, Flip Chip COB is used in high-performance lighting applications such as high-end down-lights, spotlights, and floodlights.
- Advanced Displays:Flip Chip COB is also used in advanced display technologies where high brightness, color uniformity, and compactness are critical.
- Cost-Sensitive Applications:Although generally more expensive than traditional COB, the increased performance can justify the cost in high-end applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages:
- Superior Thermal Management: Enhanced heat dissipation due to direct chip-to-PCB contact.
- Improved Electrical Performance: Lower resistance and inductance from solder bumps.
- Higher Reliability: No wire bonds to fail, leading to greater mechanical stability.
- Compact Size: Smaller form factor due to elimination of wire bonds.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: More complex manufacturing processes and materials lead to higher production costs.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Requires precise alignment and handling of solder bumps, making the manufacturing process more intricate.
- Technology Maturity: Newer technology compared to traditional COB, which may mean fewer options for certain applications or configurations.
Overall, Flip Chip COB technology is a high-performance solution that addresses many of the limitations of traditional COB by providing better thermal management, electrical performance, and reliability, making it suitable for high-end and demanding applications.
Comparison between Traditional COB and Flip Chip COB
Certainly! Here’s a point-wise comparison between traditional COB and Flip Chip COB in RGB LED applications:
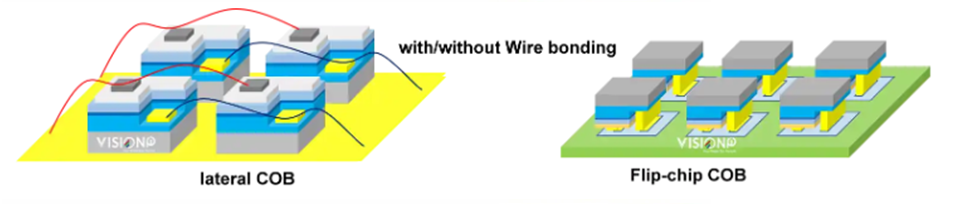
1.Chip Placement
- Traditional COB:The LED chips are mounted directly on the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) with wire bonding to connect the chip to the circuit.
- Flip Chip COB:The LED chips are flipped upside down and mounted directly on the PCB with solder bumps for electrical connections.
- Thermal Management
- Traditional COB:Thermal management relies on the thermal conductivity of the PCB and the use of heat sinks. The wire bonds can introduce thermal resistance.
- Flip Chip COB:Typically provides better thermal management since the heat can be efficiently conducted through the solder bumps and the back of the chip, reducing thermal resistance.
3.Electrical Performance
- Traditional COB:Electrical connections are made using wire bonds, which can introduce inductance and resistance, potentially affecting performance.
- Flip Chip COB:Offers lower electrical resistance and inductance due to direct connections via solder bumps, leading to improved electrical performance.
- Reliability
- Traditional COB:Wire bonds are susceptible to mechanical stress and thermal cycling, which can lead to reliability issues over time.
- Flip Chip COB:Generally offers higher reliability as the flip chip technology eliminates the need for wire bonding, reducing potential failure points.
- Manufacturing Complexity
- Traditional COB:Relatively simpler and more established manufacturing process, but involves wire bonding which adds complexity to the assembly.
- Flip Chip COB:Requires advanced manufacturing techniques and precise alignment of solder bumps, making it more complex and potentially more expensive.
6.Package Size
- Traditional COB:Larger package size due to the space required for wire bonding and additional components.
- Flip Chip COB:More compact package as it eliminates the need for wire bonds and can be directly mounted on the PCB.
7.Performance Efficiency
- Traditional COB:May have slightly lower performance efficiency due to thermal and electrical losses associated with wire bonds.
- Flip Chip COB:Typically offers higher performance efficiency due to better thermal management and reduced electrical losses.
- Cost
- Traditional COB:Generally lower cost due to simpler manufacturing processes and mature technology.
- Flip Chip COB:Often higher cost due to advanced technology and the need for precise manufacturing techniques.
9.Brightness and Color Uniformity
- Traditional COB:May exhibit slight variations in brightness and color uniformity due to wire bonding and thermal management issues.
- Flip Chip COB:Provides better color and brightness uniformity as the improved thermal management and electrical connections contribute to consistent performance.
- Applications
- Traditional COB:Commonly used in general lighting and less demanding applications where cost is a critical factor.
- Flip Chip COB:Preferred in high-performance applications requiring superior efficiency, reliability, and compactness, such as high-end displays and advanced lighting solutions.
Each technology has its own set of advantages and tradeoffs, and the choice between traditional COB and Flip Chip COB will depend on specific application requirements and cost considerations.
At AET LED Displays, we’re passionate about the LED displays industry, and we hope this article has provided valuable insights for you. Follow our blogs for more in-depth knowledge, and the latest updates in the LED display industry. Thank you once again for being part of the AET community.
For more product information, visit ;- https://aetdisplays.com/ or Send us your inquiries at sales@aetled.com
To know more about the latest updates, follow our LinkedIn page:- https://www.linkedin.com/company/aet-displays-limited/































0 Comments